
Language is the medium through which human beings interact with one another, and it is what forms the base of our society. Language complexity lies in the way that it can convey numerous ideas, feelings, and information. Of the general principles that language is built around, one such general principle is the structure, and this is made up of various elements such as adjectives, nouns, and verbs. These elements, or what we can term as the building blocks, play a very important role in the construction of sentences and the overall text framework. The role that adjectives, nouns, and verbs play in texts, their function, and their impact on the interpretation by the reader is discussed in this essay.
The Foundation of Sentences: Nouns
The most basic among the language elements is the noun, as it constructs the people, places, things, or ideas around which a sentence is framed. They construct the subject and object in a sentence and provide the base on which the meaning is constructed. In any composition, the nouns play a compulsory role in constructing the context and laying the base for the ideas being dealt with.
For example, in the sentence “The cat chased the ball,” “cat” and “ball” are both nouns. They give the central components in the sentence, and in their absence, the sentence would be empty and lacking in meaning. Nouns also assist in establishing the relationship among the components in a sentence. In the above example, the relationship between the cat and the ball is clear since the dog is pursuing the ball.

There exist various categories of nouns, including proper nouns, which represent specific names for things, people, or places (e.g., “John,” “London,” “The Eiffel Tower”), and common nouns, which represent general names for categories or classes of things (e.g., “dog,” “city,” “building”). Nouns can be count or uncountable (or non-count), depending on whether they can be counted (e.g., “three apples” vs. “happiness”). A good awareness of various categories of nouns and their application is important in forming coherent and meaningful sentences in texts.

Adjectives: Using Color and Detail
Whereas the noun is the building block that forms sentences, adjectives are the terms that provide shades of color and depth in the image that is being painted by the words. Adjectives, in their turn, are descriptive words, modifying, or altering, the nouns, providing additional information about their characteristics, attributes, or status. With the addition of adjectives in a sentence, a sentence becomes more vibrant, more engaging, and more descriptive.
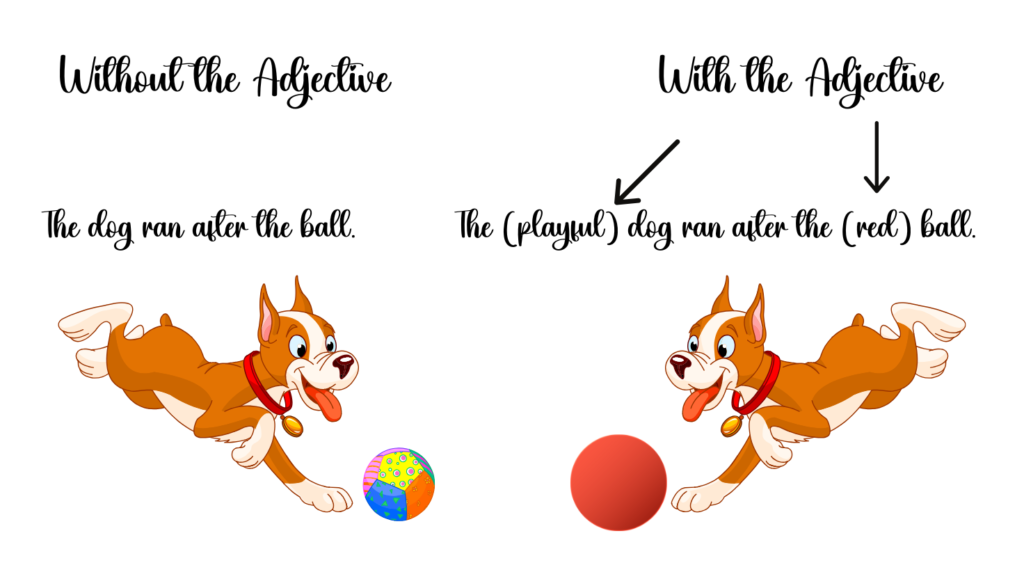
For instance, in the sentence “The dog ran after the ball,” we can add adjectives so that we can build a more vivid and appealing image: “The playful dog ran after the red ball.” “Playful” and “red” in this sentence are adjectives that provide us with more information about the cat and the ball, respectively. Adjectives can be utilized so that we can make comparisons (e.g., “bigger,” “faster,” “more beautiful”) or so that we can convey degrees in a quality (e.g., “very,” “quite,” “somewhat”).
Adjectives make writing more vibrant and more appealing to the reader. They allow the author to paint more vivid descriptions and evoke feelings, thereby making the work more memorable and more impactful. Adjectives should, however, be applied in moderation since excessive usage would make sentences too burdensome or heavy, thereby confusing or distracting the reader.

Verbs: Action and Movement in Sentences
The third linguistic building block is verbs, which establish movement and activity in sentences. Verbs tell us what the subject of the sentence is performing or what is happening with the subject. Verbs help convey the events, actions, and conditions being told in the text and help build a sense of progression and change in the text.
The action verb “chased” in “The cat chased the ball” informs us about what the cat is doing and gives the sentence direction and movement. Verbs exist in various categories, ranging from action verbs (“run,” “jump,” “think”), linking verbs (“is,” “are,” “seem”), and helping verbs (“has,” “have,” “will”). Knowing the category of verbs and their function assists one in composing strong, active, and engaging sentences in texts.

Verbs assist in establishing tense in a sentence, which conveys when the action described is occurring (e.g., the past, the present, or the future). Using the correct verb tense is important in ensuring consistency and readability in any piece, since it enables the reader to track the sequence and timing described in events.

Briefly, verbs, nouns, and adjectives are the basic building blocks of language, essential to sentence structure and text coherence. Nouns supply the skeleton of sentences, establishing context and relationships among things. Adjectives supply the color and background detail in the picture painted by words, rendering texts more descriptive and interesting. Verbs supply the action and motion in sentences, expressing the events, actions, or states represented. Together, they compose a dynamic, multifaceted, and important language that helps authors convey precise ideas, feelings, and information in writings. The use and meaning of nouns, adjectives, and verbs must be familiar to anyone wishing to construct coherent, engaging, and successful writings.